What is the Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)? The Ultimate Guide
September 16, 2024 · 10 min read
In the world of project management, where the success of a project hinges on meticulous planning and flawless execution, the Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) emerges as an essential tool.
What is RTM?
Once you have a solid set of requirements, the next step is to organize them into a requirement matrix. This matrix is a visual representation of all project requirements, linking each one to project deliverables, timelines, and responsible parties.
Types of Traceability Matrix
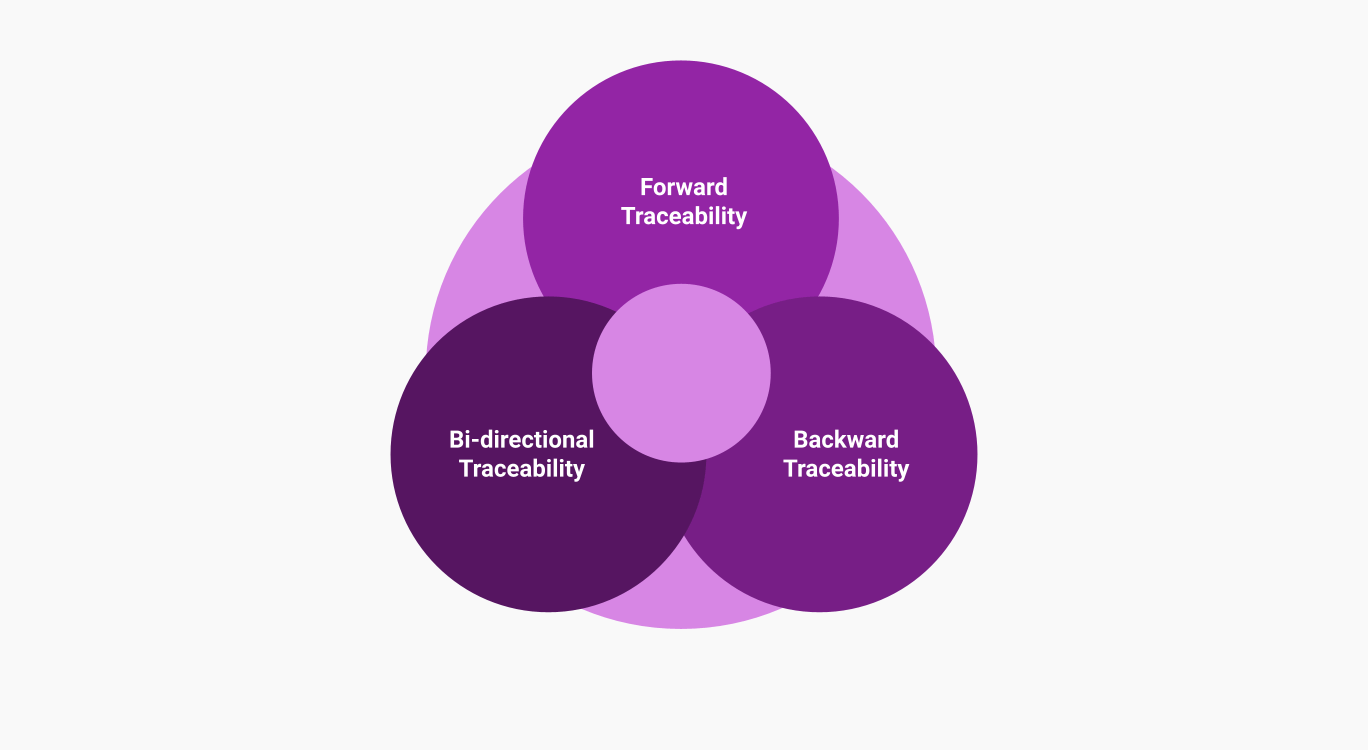
Depending on your project’s needs, you might encounter different types of RTMs:
- Forward Traceability. Tracks the progress of requirements to ensure they are included in the final product. It’s like looking forward, making sure all requirements are addressed.
- Backward Traceability. Ensures that the final product traces back to the original requirements, confirming that nothing extra has been added. It’s like retracing your steps to ensure accuracy.
- Bidirectional Traceability. Combines forward and backward traceability, providing a comprehensive view that ensures all requirements are met and nothing unnecessary is included.
What Does the Requirement Matrix Include?
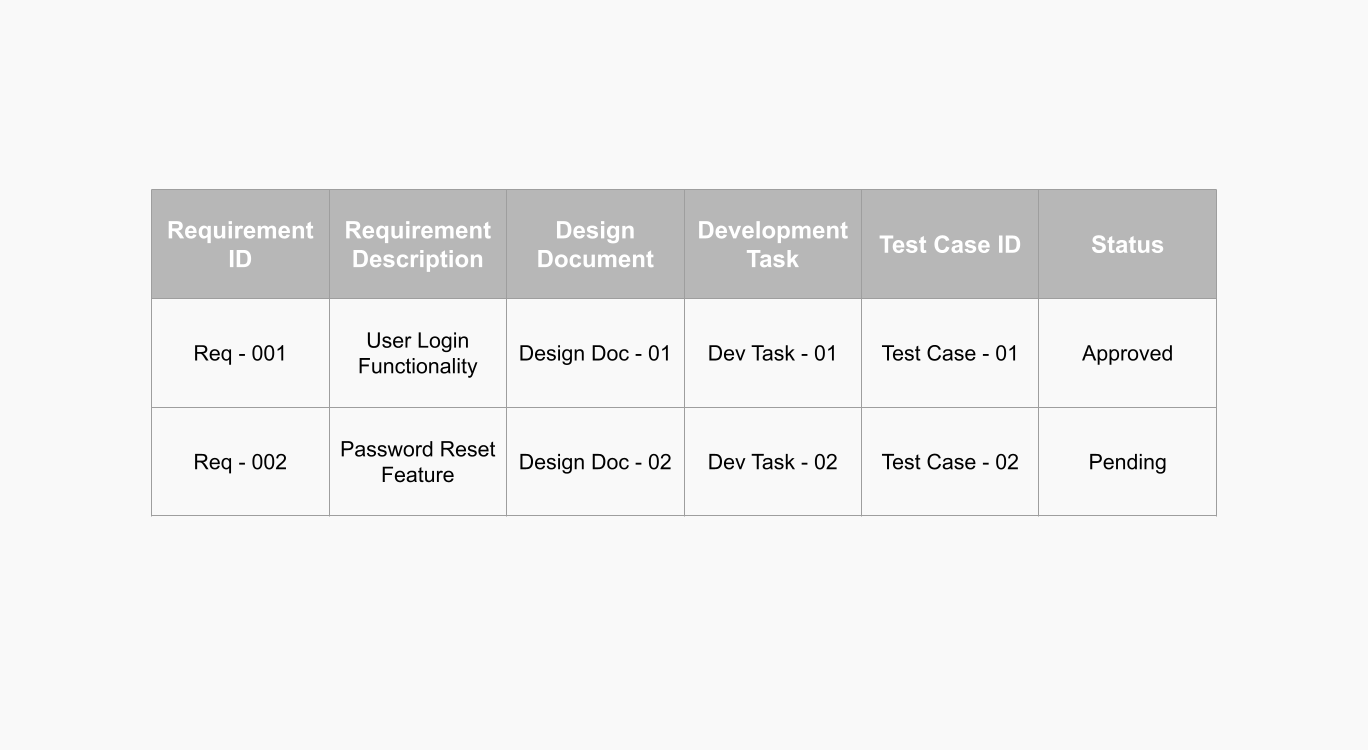 A typical Requirements Matrix usually contains the following elements:
A typical Requirements Matrix usually contains the following elements:
- Requirement Description. A clear and concise explanation of the requirement.
- Author and Contributor. Who originally provided the requirement and who entered it into the matrix.
- Date of Identification. When the requirement was identified.
- Source Document. The document or source where the requirement was initially captured.
- Requirement Status. The current state of the requirement (e.g., pending, in progress, completed).
- Specification. Detailed specifications or technical details related to the requirement.
- Implementation Date. The planned or actual date when the requirement was implemented.
- Acceptance Date. When the requirement was accepted and validated by the relevant stakeholders.
How to Create a Traceability Matrix?
Creating an RTM might sound like a daunting task, but with a structured approach, it can be quite straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify and Document Requirements. Begin by gathering and documenting all project requirements. This will serve as the foundation of your RTM.
- Define Traceability. Determine the type of traceability needed (forward, backward, bidirectional). This decision will shape how your matrix is structured.
- Set Up the Matrix Structure. Typically, an RTM is structured with rows representing requirements and columns representing different stages of the project (e.g., design, development, testing).
- Populate the Matrix. Link each requirement to its corresponding deliverable, design component, and test case. This is the core of your RTM, where every requirement is connected to its lifecycle stages.
- Assign Responsibility. In the matrix, designate a responsible party for each requirement. This accountability ensures that each requirement is addressed by someone who will oversee its completion.
- Review and Update Regularly. An RTM is a living document. Regular updates and reviews are crucial to ensure it remains accurate and relevant throughout the project lifecycle.
Requirements Traceability Matrix Tools
The term "matrix" here is more conceptual; while it can be represented in a table format, modern tools like task trackers (e.g., Planyway) are increasingly popular for this purpose. The key criterion is that this information should be easy to access and understand for all team members. Everyone involved should have access to this matrix, and it should clearly record everything important about each requirement.

Several tools can assist in creating and maintaining an RTM, making the process more efficient and less prone to errors:
- JIRA. A powerful tool for managing requirements, JIRA’s integration capabilities allow you to create a traceability matrix that links requirements to tasks, tests, and defects.
- IBM Rational DOORS. Specifically designed for requirements management, this tool offers robust traceability features, making it a popular choice for large-scale projects.
- ReQtest. An easy-to-use tool that helps in creating traceability matrices, ReQtest is particularly useful for teams looking to manage requirements, tests, and defects in a single platform.
- MS Excel. For smaller projects, a well-structured Excel sheet can serve as an effective RTM, offering flexibility and simplicity.
Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) Template
Getting started with a Requirements Traceability Matrix Template can significantly streamline your workflow. Here’s a basic structure you can use:
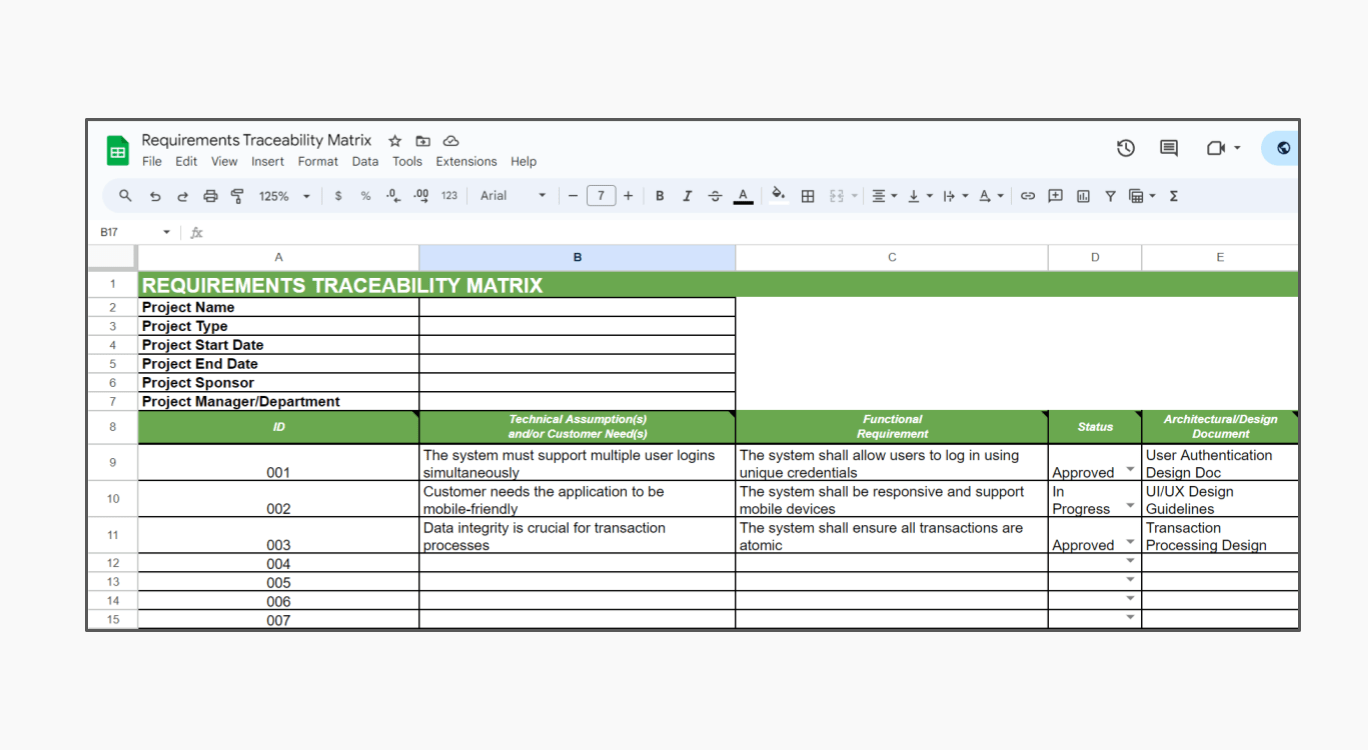
This template provides a starting point. You can customize it to fit the specific needs of your project, adding columns for risk levels, priority, or other relevant details.
Benefits of RTM
Imagine trying to assemble a complex puzzle without the picture on the box. The RTM provides that picture, ensuring that every piece (requirement) fits exactly where it should. Here’s how RTM adds value:
- Clarity and Alignment. RTM ensures that every requirement is accounted for, tracked, and aligned with the project objectives. It’s a beacon of clarity amidst the chaos.
- Risk Mitigation. By providing a clear traceability path, RTM helps in identifying and addressing potential gaps or conflicts in requirements early in the project, significantly reducing the risk of errors.
- Efficient Change Management. When changes occur (and they will), RTM helps assess the impact of those changes across the project, ensuring that modifications are implemented smoothly and nothing crucial is overlooked.
- Enhanced Communication. RTM acts as a communication bridge between stakeholders, developers, and testers, ensuring that everyone is on the same page.
- Quality Assurance. By linking requirements to test cases, RTM ensures that every requirement is validated, contributing to a higher quality of the final product.
Conclusion
The Requirements Traceability Matrix is more than just a document; it’s a strategic tool that ensures your project stays on track from inception to delivery. By investing time in creating and maintaining an RTM, you’re not just keeping tabs on requirements—you’re safeguarding your project’s success. Whether you’re managing a small project with a simple Excel sheet or a large-scale initiative with advanced tools, an RTM can be your key to delivering high-quality, requirement-compliant outcomes.
About the Author
Sergey Koshevoy is the CEO of Planyway and a seasoned product manager, bringing a wealth of experience in project management and team collaboration tools. A fan of productivity techniques, Sergey is passionate about creating intuitive and efficient solutions that help teams work smarter and achieve their goals.


